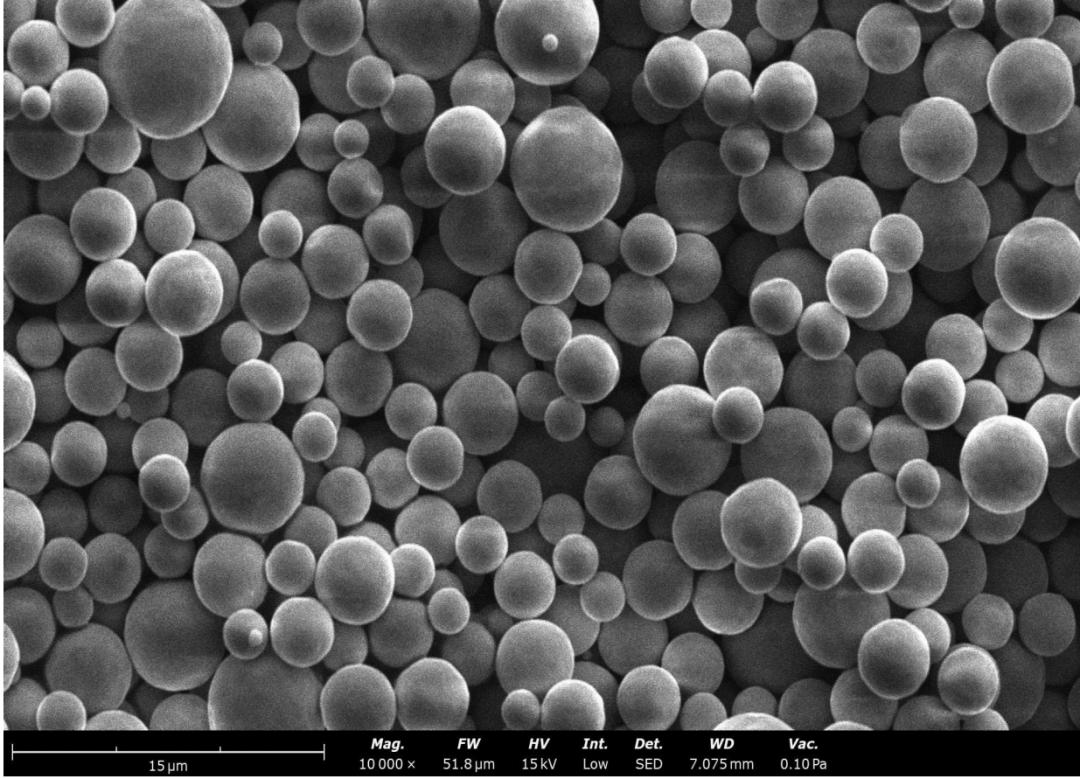
Ultra-fine powder is applied to head AI chips. Zhejiang's key specialized and sophisticated "little giant" enterprise "Xinchuan New Materials" secures 50 million yuan in Series B+ financing | Exclusive from 36Kr
Text | Zhang Bingbing
Editor | A Zhi
36Kr learned that Hangzhou Xinchuan New Materials Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Xinchuan New Materials") recently announced that it has received a Series B+ financing of 50 million yuan, led by Zhejiang Venture Capital and followed by Kefa Capital. The funds from this round will be mainly used for the development and mass production of new electronic components and core materials for photovoltaics, as well as the construction of a new phase of production capacity.
Founded in August 2017 and headquartered in Xiaoshan District, Hangzhou, "Xinchuan New Materials" is committed to becoming a global basic materials company for electronic information and green energy. Its self-developed nickel powder for internal electrodes of MLCC (Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor) has solved the problem of domestic production of high-end MLCC internal electrode materials. Its "High-end finished nickel powder below 200nm for MLCC internal electrodes" was listed as a new industrial product in Zhejiang Province in 2024 and was recognized as the "first batch in China".
Currently, "Xinchuan New Materials" has achieved mass production of nickel powder for MLCC and ultra-fine soft magnetic powder for AI, and is continuously promoting the large-scale application of high-end powder materials such as photovoltaic copper powder and base metal catalysts for hydrogen production, covering application fields such as electronic information, green energy, automotive electronics, and communications. In 2025, "Xinchuan New Materials" was included in the list of specialized and sophisticated small and medium-sized enterprises with strong innovation capabilities in Zhejiang Province.
Filling the gap in finished nickel powder, achieving stable mass production at low cost and gaining market recognition
MLCC is currently the most in-demand electronic component and an indispensable basic component in integrated circuits. It ensures the stable operation of electronic devices and is widely used in fields such as smartphones, 5G base stations, and new energy vehicles. Nickel powder has become the core material for MLCC internal electrodes due to its characteristics such as high sphericity, high dispersion, high conductivity, oxidation resistance, and strong heat resistance.
Currently, Japan and South Korea account for more than 70% of the MLCC market share, and correspondingly, Japanese companies dominate the nickel powder supply market. Among domestic nickel powder suppliers, Boqian New Materials is the leader. A relevant report by Southwest Securities in 2022 showed that Boqian New Materials' main products include semi-finished graded nickel powder of 80nm, semi-finished graded nickel powder of 300nm, and finished graded nickel powder of 300nm. For some time, there was a gap in domestic graded finished nickel powder below 200nm, especially in the specifications of 80nm - 120nm.
Driven by market demand, "Xinchuan New Materials" shifted its R & D focus from 3D printing powder to nickel powder in the second half of 2018. In April 2020, it officially launched the first equipment for mass-producing ultra-fine powder, and by 2022, its 150nm finished nickel powder product passed customer certification and began mass production, which went through a difficult technological breakthrough stage.
When talking about the technological difficulties, Xie Shangchuan, the founder of "Xinchuan New Materials", said that the first difficulty was how to ensure efficient and stable production: "If mass production cannot be achieved, customers will not even try the product, and subsequent R & D and market promotion cannot be carried out."
The key for "Xinchuan New Materials" to achieve mass production is the self-developed and upgraded evaporation-condensation powder-making process. Generally speaking, the evaporation-condensation method is to heat the metal to its boiling point for evaporation and then cool it into powder. In essence, there are only two processes - heating and cooling. The core difficulty of the process is how to automate these two processes and achieve stable control.
Xie Shangchuan introduced: "We have developed a brand - new process control system for evaporation and condensation, including temperature field control, thermal balance control, and rapid cooling process control. In particular, we have developed a controllable rapid cooling process, which has achieved ultra - high - speed cooling, enabling the rapid generation of powder, improving the overall production efficiency and yield rate, and achieving stable mass production."
Xinchuan New Materials' production workshop
The second difficulty is the classification treatment after producing ultra - fine powder. In the nickel powder production process, "classification" is a key subsequent deep - processing link, which directly determines whether the nickel powder product can be accepted by the market. The core of classification lies in the fine separation of the original powder according to particle size, removing large particles, so as to obtain finished powder products of different specifications.
"Especially in the electronics industry, which is highly price - sensitive, fine screening and classification need to be carried out while controlling costs." Xie Shangchuan further explained, "The core difficulty in classifying nickel powder below 200nm is how to efficiently remove large particles while considering costs."
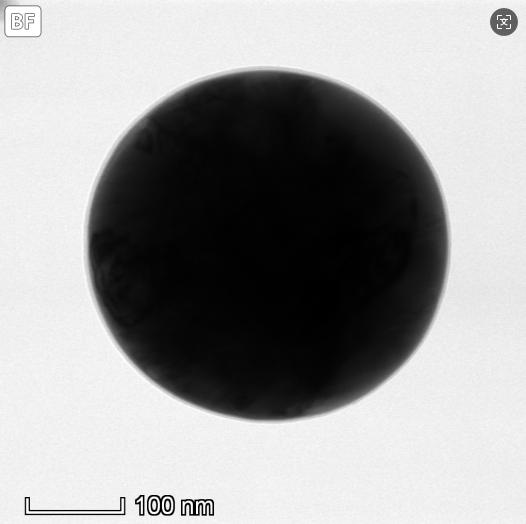
High - magnification TEM photo of Xinchuan New Materials' nickel powder
It is reported that through technological breakthroughs, "Xinchuan New Materials" has achieved the classification of 150nm and 200nm nickel powder. In 2025, it developed a new nano - scale nickel powder cooling process and classification process, further improving the productivity and yield rate. "Xinchuan New Materials" has developed 80 - 120nm finished graded nickel powder with a cutting particle size of 400nm and below, and can coat a certain thickness of ceramic film on it to improve the dispersion of nano - scale nickel powder and delay its sintering temperature. It can match MLCC with a ceramic film thickness of 0.8μm and below. Compared with nickel powder of the same specification in the market, it can reduce customers' procurement costs by more than 30%.
The markets for MLCC and various electronic components are mostly in Japan and South Korea. As a producer and supplier of their basic core materials, going global is an inevitable choice for "Xinchuan New Materials". However, entering the Japanese and South Korean markets is a great test for the company's quality management ability, R & D ability, and service ability.
In 2022, Japan's Inahata Sangyo Co., Ltd. completed a strategic investment in "Xinchuan New Materials", providing key support for its expansion into the Japanese market. Xie Shangchuan introduced that in 2024, "Xinchuan New Materials" was officially included in the supply chain system of mainstream Japanese component manufacturers. As of now, "Xinchuan New Materials" has received bulk purchase orders from multiple customers in Japan, South Korea, and China. The overall sales volume has been continuously increasing, and it has achieved positive cash flow since 2024.
From AI to photovoltaics, researching ultra - fine powder materials in multiple fields
In addition to its core product of nickel powder, in the face of the booming markets of AI and new energy, "Xinchuan New Materials" is also continuously expanding its range of high - end powder materials.
In high - end application scenarios such as AI server power modules and in - vehicle high - wire harness millimeter - wave radars, inductors need to meet the dual requirements of high - frequency instantaneous response and low magnetic loss. Ultra - fine soft magnetic powder has become an essential material to meet this performance requirement due to its high magnetic permeability, low loss characteristics, and excellent temperature stability, and is widely used in high - frequency inductor components.
It is reported that "Xinchuan New Materials" started researching ultra - fine soft magnetic powder in 2021 and has now achieved industrial production. It is specially used for inductors in AI servers and is applied to the AI servers of leading chip manufacturers, with a sales scale in the hundreds of tons.
In the photovoltaic industry where cost is king, Xie Shangchuan believes that what restricts the cost per watt of photovoltaic wafers is not only the equipment but also the slurry consumption of battery wafers. Currently, silver paste is mainly used for battery wafer slurry. However, considering the current situation of the entire photovoltaic industry and factors such as the silver price, the replacement of silver with silver - coated copper and pure copper powder can significantly reduce costs.
"The time for copper to replace silver has come." The copper powder used in photovoltaics has extremely high requirements for cleanliness, sphericity, and particle size distribution stability. The copper powder produced by our evaporation - condensation method is just suitable, and combined with our classification advantage, it can perfectly meet the requirements of photovoltaic copper powder. Therefore, after 2024, pure copper powder for photovoltaics and copper powder for silver - coated copper have become new products that "Xinchuan New Materials" focuses on promoting.
"But ultimately, the degree of copper powder use in the photovoltaic industry depends on the downstream, such as the R & D progress of copper powder by photovoltaic power station and photovoltaic module manufacturers." Xie Shangchuan predicts that the photovoltaic copper powder market will see a significant increase in the next two to three years.
SEM photo of Xinchuan New Materials' photovoltaic copper powder
In terms of industrial layout, Xie Shangchuan frankly said that as a startup company, the business environment, entrepreneurial environment, and government services need to be considered first. Therefore, "Xinchuan New Materials" has set up its headquarters in Xiaoshan, Hangzhou, integrating a R & D center, a sales center, and a production center. At the same time, considering factors such as customer supply safety and production scale expansion, "Xinchuan New Materials" has also laid out a production base in Liandu, Lishui. In 2025, "Xinchuan New Materials" plans to achieve a production capacity of 1,500 tons of ultra - fine metal powder. It is expected that the production capacity will increase to 2,000 - 2,500 tons in 2026, and depending on the market situation, it will choose the right time to build a third base.
In terms of product planning, based on the industry development direction, in addition to MLCC nickel powder, AI ultra - fine soft magnetic powder, and photovoltaic copper powder, "Xinchuan New Materials" will also research base metal catalysts for hydrogen production, give full play to the role of basic materials, cooperate with the development of the industrial chain, and strive to become a global basic materials company for electronic information and green energy.
36Kr Future Industries
"36Kr Future Industries" continuously focuses on urban development, industrial transformation, and the implementation of innovation and entrepreneurship projects. For media coverage, you can contact wangfengzhi@36kr.com by email or scan the code to contact the author.
In addition, 36Kr officially launched the "36Kr Enterprise Investment Guide Internal Reference" this year. Relying on its in - depth accumulation in the economic circle industrial cluster, regional key promotion plans, and investment promotion fields, 36Kr provides in - depth, detailed, timely, and exclusive comprehensive information services to government departments, providing them with efficient and accurate industrial project internal references; helping project parties match industrial funds, connect with key contacts, and quickly integrate into the new industrial ecosystem.
This article is from the WeChat public account "36Kr Future Industries". Author: Zhang Bingbing, A Zhi. Republished by 36Kr with permission.