The "AI Zhang Xuefengs" of big tech companies have taken up their posts. This is a major training exercise for Agent products.
Text by | Deng Yongyi
Edited by | Su Jianxun
Shortly after the 2025 college entrance examination ended, another "battlefield" - the college entrance examination volunteer filling - kicked off.
After the popularity of ChatGPT, the most popular AI test is to let AI complete what humans have studied hard for many years - various test questions, including those in the high school entrance examination, college entrance examination, and even Olympic competition questions, to experience how "smart" AI is.
It's easy to find that by 2025, for both major model manufacturers and the media, making AI do test questions is no longer the focus. This is no longer very difficult for AI. Instead, it's the college entrance examination volunteer filling.
The college entrance examination volunteer filling market has always been one with high information barriers and low concentration. Zhang Xuefeng, who became popular due to live - streaming, quickly entered the public view because his views "broke the information gap" and expanded the market. Data from iiMedia Research shows that the paid scale of the college entrance examination volunteer filling market in China reached 950 million yuan in 2023, a 7.3 - fold increase compared with 2016, and it is expected to reach 1.22 billion yuan in 2027.
But this year, Zhang Xuefeng, who was caught in an public opinion storm, stopped his live - streaming for two months during the college entrance examination season and may never appear in public again. And the "AI Zhang Xuefeng" of the big tech companies quickly filled this gap.
On June 12, "Quark", an AI application under Alibaba, officially launched the "College Entrance Examination Volunteer Big Model" and the "College Entrance Examination Knowledge Base", and simultaneously launched three functions: "In - depth College Entrance Examination Search", "Volunteer Report", and "Intelligent Volunteer Selection".
In its external introduction, Quark said that this model "can think like a volunteer expert" and provide accurate and personalized volunteer filling assistance services for each candidate.
To put it simply, Quark trained a big model for college entrance examination volunteer filling based on Alibaba's flagship big model, "Tongyi Qianwen". Candidates only need to input a description of their scores, preferences for colleges/majors/regions, and the model will go through a series of thinking and analysis to generate an "AI Volunteer Report", a complete report covering strategies such as "striving for the best, ensuring a stable choice, and having a backup option", a volunteer form, and college and major recommendations.
△Source: Quark
College entrance examination volunteer filling is a low - frequency but essential scenario. Due to its great influence, search engine companies entered this scenario many years ago, providing information screening, searching, and analysis services for candidates and parents.
The players in this scenario also include offline "college entrance examination volunteer filling" institutions that have been established for many years, such as Jingzhiyuan, Bainian Yucai, Youzhiyuan, etc., as well as education giants like New Oriental, Yuanfudao, and Zuoyebang, which have also launched volunteer filling services.
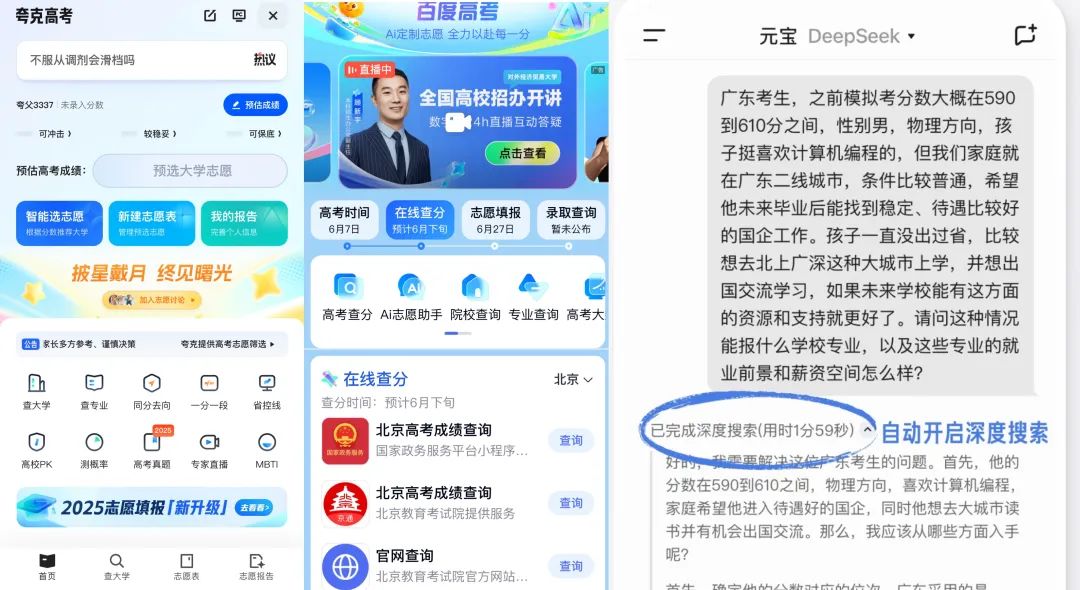
This may also be the reason why college entrance examination volunteer filling has become a new battlefield for big tech companies' AI products. During the college entrance examination season, companies including Alibaba's Quark, Tencent's QQ Browser/Yuanbao, and Baidu have all launched key products and services related to the college entrance examination.
△Illustration: From left to right, they are Quark, Baidu, and Yuanbao's college entrance examination volunteer filling products. Chart by 36Kr.
However, except for a few paid services, most of the college entrance examination - related services launched by big tech companies remain free, maintaining a considerable public - welfare nature. But for big tech companies, this is also a rare opportunity for a traffic peak and building a good reputation.
At the press conference, Quark revealed several figures: In the past seven years, Quark's college entrance examination services have served a total of 120 million candidates. In 2024 alone, more than 30 million candidates used Quark's services.
From AI taking the college entrance examination to AI assisting in volunteer filling, the model's capabilities have been greatly improved
What's the difference between making AI take the college entrance examination and having AI assist in volunteer filling?
Making AI take the college entrance examination is a one - time action. Users only need to take a photo of the questions or manually input them into the dialog box to get the answers.
But volunteer filling is different. In 2025, the number of national college entrance examination candidates reached 13.35 million, second only to the historical peak. With candidates' anxiety about getting into good universities and majors remaining high, how to fill in the volunteers is a more complex strategic combination.
From the data perspective, candidates and parents need to understand a huge amount of data in the short few days of volunteer filling.
For example, the rules and policies vary greatly from province to province. Some provinces adopt the "college + major" selection method, while others adopt the "college + major group" method. Although the new college entrance examination has been implemented for 11 years, the number of volunteers that candidates can fill in ranges from 30 to 112 in different regions. Just the admission regulations, major data, and public materials of each school already represent a huge workload.
In addition, there is also a lot of "non - public" or "semi - public" data that candidates and parents have difficulty accessing. For example, what exactly does each major teach? The employment destinations of each college, and even the thinking path for application, etc., all require long - term follow - up, observation, and accumulation. Traditional college entrance examination volunteer filling institutions often use this as a selling point to provide paid services to candidates and parents.
So, how can the big model help with college entrance examination volunteer filling?
Take Quark's "Volunteer Report" Agent as an example. This Agent is based on the candidate's scores, interests, family background, and regional preferences. It will first formulate a personalized task plan (such as positioning the score range, screening major directions, formulating filling strategies, etc.); then convert the tasks into instructions and complete the task execution based on high - quality data.
Currently, Quark's college entrance examination data knowledge base covers more than 2,900 universities and nearly 1,600 undergraduate majors across the country, and further expands to dimensions such as the employment destinations of university graduates, emerging industry trends, and the industrial structure of each city. All data comes from reliable sources and is cross - verified multiple times and manually sampled to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the content.
"College entrance examination volunteer filling is a very typical scenario for information processing and service, and it is also a scenario where the big model can play its greatest value." Zhang Fan, the person in charge of Quark's AI search, told "Intelligent Emergence".
Different from previous years, the current volunteer filling scenario is not just simply "filling in the form" and then generating a report according to the rules. Instead, it makes more full use of the big model's capabilities to solve more personalized problems.
In the process of generating the report, the model's thinking mode is already very similar to that of humans. First, the model needs to conduct a large - scale analysis of the user's situation; then determine what questions need to be retrieved - retrieve a large amount of industry and employment data. Then, the model will judge the specific matching degree of hundreds of schools and majors with the candidate and finally complete the report design.
Users can feel the difference in terms of time. If a candidate uses Quark's "Volunteer Report" function, it takes 5 - 10 minutes to generate a report.
This is because the model requires a large amount of computing power. "We have calculated that generating a volunteer report is equivalent to making tens of thousands of search actions." Jia Haifeng, the product manager of Quark, said that Quark has also prepared more than 100 times the computing power input this year to support in - depth search scenarios.
The explosion of Agent products, and unique data has become the barrier
Since its establishment in 2019, Quark has been one of the most "low - key" in the Alibaba ecosystem: it rarely holds press conferences, and the few times it has are almost all related to college entrance examination products.
Why are big tech companies now attaching so much importance to this scenario?
This has a lot to do with the explosion of agents (Agents). After the release of DeepSeek R1 brought the popularity of inference models, the AI market in 2025 entered the era of the "Battle of a Hundred Agents": In addition to big tech companies launching Agents for programming, image/video generation, data analysis, etc., many original SaaS companies are also transforming into vertical Agents, such as RPA, BI, outbound call robots, marketing SaaS companies, etc.
Vertical Agents can actually be regarded as the prototype of AI Native applications. On the one hand, these vertical Agents must be fine - tuned on the general model to "teach" the model the industry's know - how; on the other hand, unique data will become the real barrier for Agents.
In the college entrance examination scenario, a typical question is: If there is another popular volunteer filling expert like Zhang Xuefeng, will candidates' choices become more similar and homogeneous?
When it comes to the model, the same question arises: If the model has a fixed data set, will it preferentially recommend a certain major in a certain school, making candidates' choices more and more similar?
The answer is no. The thinking chain added during model training, as well as the unique data and real - time search function, will reduce the occurrence of homogenization.
During training, the Quark team added the decision - making and analysis paths of hundreds of senior human college entrance examination volunteer planners and real - life application process conversations. These volunteer planners from different regions with different styles summarized tens of thousands of real "reasoning chains" for the model - that is, the thinking and decision - making paths of application experts, which were converted into high - quality supervised data and internalized into the model.
Currently, the Quark team has completed expert annotation and scoring of thousands of volunteer reports. Through the method of "human finding faults + model correction", the model's output continuously approaches the real judgment standard of experts in terms of professionalism and matching degree.
The most obvious result is that if the same prompt words are input into the model again, different application plans with different application styles will be generated.
"Quark's volunteer report and in - depth search will generate different strategies based on each candidate's profile, scores, interests, and preferences, providing multiple options such as 'prioritizing colleges', 'prioritizing majors', and 'prioritizing cities' for users to choose from." Quark said at the meeting.
△Source: Quark
Now, from the forms of big tech companies' college entrance examination scenario Agents, it can be seen that there are clear differences in the strategies and product advantages of each company's AI products.
Quark's product idea is more like a professional tool. It has a separate module for the college entrance examination on the product homepage. In terms of promotion efforts, it can be said to be the most prominent.
The design of other college entrance examination volunteer products such as Tencent Yuanbao and Baidu is more inclined to be "embedded" in the original product form and interaction, which is more concise. For example, in QQ Browser, which is also a browser, users can only access the College Entrance Examination Agent by entering "college entrance examination" in the search box.
"Our design principle is to reach the user only when he needs it." Li Ruizhang, the person in charge of QQ Browser's AI search product, said in a media interview.
Whether it's Quark, Tencent, or Baidu, each company's AI volunteer filling product also has its own unique data. The differences between Agents are much greater than those between general big models.
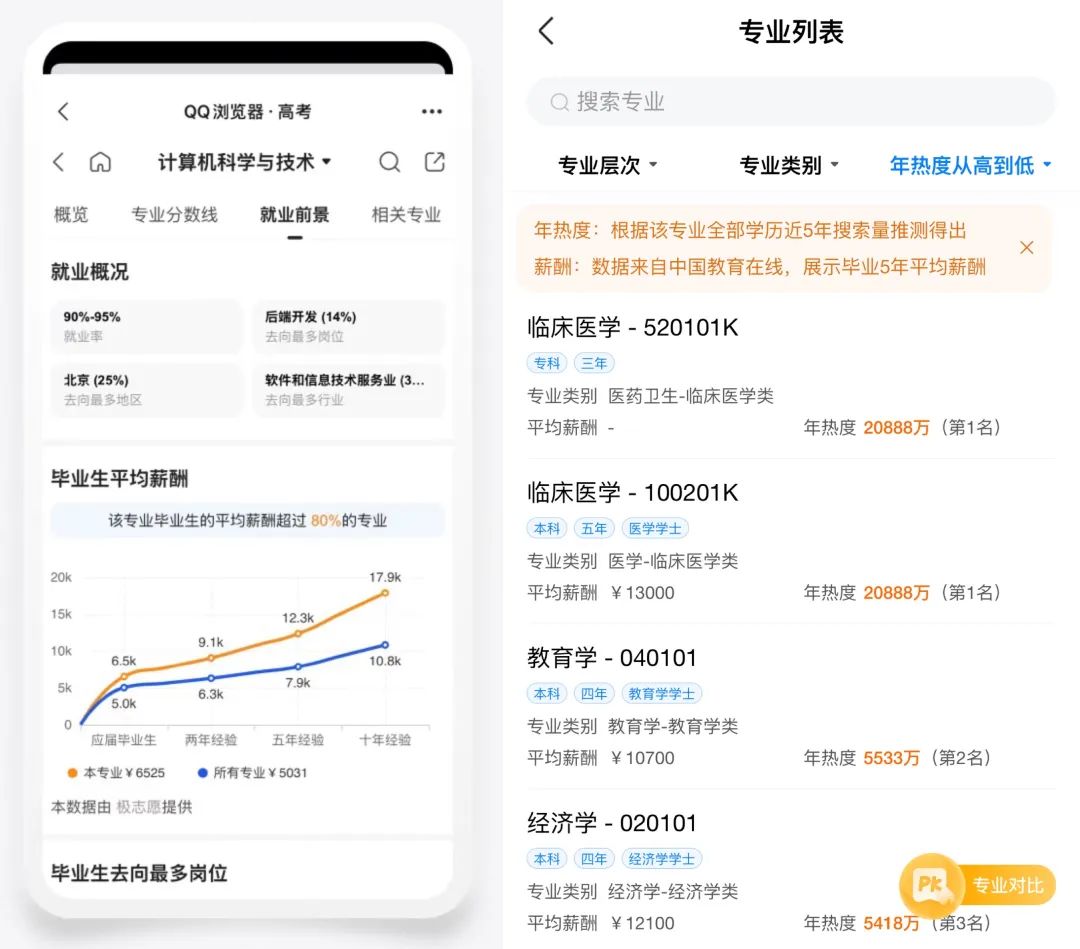
For example, QQ Browser has a strategic cooperation with the offline institution Jizhiyuan, so it can give more accurate predictions on the employment salary prospects; while Baidu has a unique "search popularity" function, which can intuitively show the search volume of colleges and majors, providing more dimensions for reference.
△QQ Browser's "average salary curve" and Baidu's "search volume to infer salary" function. Chart by 36Kr.
Ultimately, big tech companies attach great importance to low - frequency but essential scenarios like the college entrance examination mainly because the main users are young people. Most users of all current AI products are young people, who are important early adopters. If they can provide services at important nodes such as the college entrance examination and starting a job, it will greatly help AI products build "trust" with the young user group and turn them into long - term users.
Welcome to communicate
Welcome to communicate
This article is from the WeChat public account "Intelligent Emergence", author: Deng Yongyi. Republished by 36Kr with permission.