AI company Xijia Medical secures tens of millions of yuan in angel-round financing to develop a Chinese version of the Stanford therapy for depression | Exclusive from 36Kr
36Kr learned that NuraNavX, a brain science AI company, recently completed an angel-round financing of tens of millions of yuan, invested by K2 Venture Partners. The funds from this round of financing will mainly be used for the market promotion and further R & D of AI brain connectomics products. The company will launch a new round of financing in the middle of this year.
Brain connectomics studies the brain by analyzing the connections and networking patterns between brain neurons. NuraNavX's AI individualized brain network map based on brain connectomics can be simply understood as mapping the brain's GPS. Different from traditional brain imaging technologies, it reveals how different brain regions are interconnected to form a brain network, and then helps understand the functions and operating mechanisms of different brain regions. This is crucial for understanding the pathogenesis of complex brain diseases, and based on this, the company has treated more than 1,000 patients in domestic clinical settings.
"Some diseases, such as depression, autism, and severe insomnia, are not caused by organic lesions in the brain regions, but by abnormal connections in the brain functional areas," said Yuan Quan, CFO of NuraNavX.
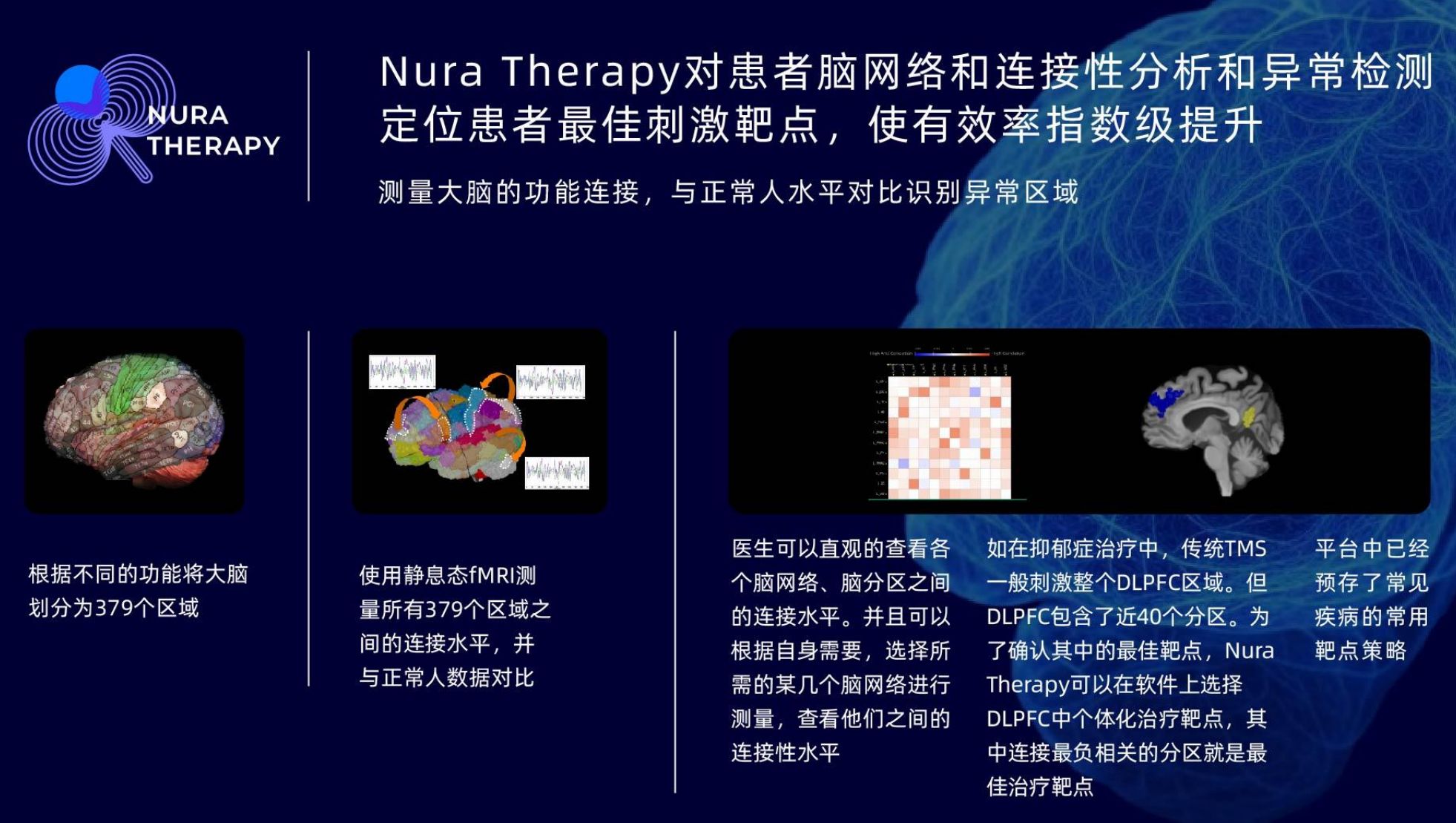
Based on MRI data, NuraNavX divides each patient's brain into 379 unique brain regions and studies and summarizes more than 20 important brain functional networks through the nerve fiber bundles connecting each partition. "Through our original SCA (Structural Connectivity Atlas), we can generate a personalized brain network map for each patient, which can be used for the protection of brain functional areas in neurosurgical operations, as well as the targeting and precise treatment of central nervous system diseases such as depression and anxiety."
Nerve fiber bundles can be understood as the "wiring" in the brain that connects different brain regions. The SCA technology uses machine learning to extract the structural features of nerve fiber bundles and uses data from healthy and diseased subjects for learning and verification, ultimately forming a brain network model with good generalization and high accuracy. Due to the differences in each person's brain size and even the displacement of brain regions caused by brain diseases, the brains of clinical patients are "unique to each individual." The SCA technology can restore the specificity of the patient's brain, enabling the generation of an individualized brain network structure model for each patient, which can be used for neurosurgical operation planning.
In the scenario of neurosurgical operations, one of the challenges faced by surgeons is to remove tumors and other lesions as completely as possible while avoiding damage to the patient's important brain functional areas to ensure a normal post - operative life. The whole process is truly a matter of "a miss is as good as a mile." NuraNavX's Nura Surgical software automatically presents the patient's brain network and the surrounding fiber bundles, clarifies the specific functional networks to which the fiber bundles belong, helps doctors evaluate the importance level of the fiber bundles, and provides support for doctors to formulate surgical resection paths.
More importantly, in addition to accurately mapping traditional functional networks such as those related to movement and language, NuraNavX has located multiple non - traditional high - level functional networks based on brain connectomics. These networks are responsible for the brain's high - level cognitive functions, such as memory, analytical ability, and emotions. Based on this, it can help neurosurgeons better understand brain tumors and functional networks and optimize surgical approaches to protect the patient's functional networks and high - level cognitive functions.
It is reported that at the end of 2023, NuraNavX obtained the first Class II medical device registration certificate in China, and its neurosurgical operation planning product has also entered several top - tier hospitals in China. "Overseas, Nura Surgical has entered the neurosurgery departments of 120 hospitals and has been used in more than 10,000 neurosurgical operations in total," said Yuan Quan. The AI brain network map is driven by data and algorithms. The real - world data such as cases and operation plans accumulated during the application process will continuously feed back to the AI model, providing the possibility for software iteration and generating a data flywheel effect.
The targeting logic of NuraNavX
In addition to its application in neurosurgery, the AI brain connectomics system also shows considerable potential in the neuromodulation treatment of brain functional diseases.
Since the development of modern medicine, there have been continuous attempts to overcome diseases such as depression, anxiety, autism, and schizophrenia. However, there are still many clinical pain points for these diseases. Firstly, the diagnosis lacks objectivity and relies on scale assessments and doctors' experience. Secondly, in terms of treatment, drug therapy has certain side effects and lacks personalization. Patients need to try multiple drugs to find a suitable treatment plan. Therefore, there is an urgent clinical need for medical products that can objectively diagnose and precisely treat such diseases.
It is understood that to overcome depression, Stanford University pioneered the "Stanford Protocol" for precise transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). Simply put, through the analysis of functional connectivity magnetic resonance data, the key brain regions of patients are identified, personalized targets are located, and TMS stimulation of a certain intensity and frequency is applied to help patients relieve depressive symptoms.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a well - established treatment method that has been approved for the treatment of depression both at home and abroad. The advantage of traditional TMS is that it is safe and non - invasive, while the disadvantage is the lack of precise targeting, resulting in a relatively low clinical effective rate. The Stanford Protocol proposes a precise, high - dose accelerated TMS treatment plan based on fMRI navigation. The area with the most negative correlation between the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) and the subgenual anterior cingulate cortex (sgACC) is used as the target. Targeted TMS treatment is carried out 10 times a day, with 1,800 pulses each time, for a total of 5 days. In a double - blind trial, it achieved a 79% treatment effective rate for drug - resistant and treatment - refractory patients and has now been included in the US medical insurance.
"The Stanford Protocol has shown high clinical effectiveness for treatment - refractory depression," said Yuan Quan. However, it is only a treatment plan specifically for depression and not a mature software for identifying individualized targets in patients, so it has limitations in clinical application. At present, some domestic hospitals have introduced similar therapies, but they are mainly used for scientific research. The target calculation of many software takes several days, which limits large - scale clinical application. In contrast, NuraNavX's AI brain network map software only takes 1 - 1.5 hours to calculate the individualized treatment target plan for patients.
Moreover, based on brain science research and the accumulated data and cases, in addition to treatment - refractory depression, "this software can also play a role in calculating the targets for other diseases such as anxiety disorders, sleep disorders, schizophrenia, autism, tic disorders, Alzheimer's disease, and stroke rehabilitation. Through the same underlying technology and AI platform, we can calculate the precise targets related to the above - mentioned diseases and present the strategic logic of target calculation to doctors to support them in formulating treatment plans."
TMS, as a mature and non - invasive stimulation treatment plan, has been around for a long time. However, to achieve good curative effects, the brain target area for stimulation must be accurate, and the frequency and intensity of stimulation need to be appropriate. Otherwise, it may be ineffective or even have negative effects.
At present, NuraNavX is cooperating with top - tier hospitals such as Beijing Anding Hospital to conduct larger - scale clinical trials on the auxiliary diagnosis and treatment of some severe mental diseases to support further prospective research.
"In terms of commercialization, we have established self - operated neuromodulation clinics in Shenzhen and Shanghai to provide treatment for patients with depression, anxiety, insomnia, childhood autism and hyperactivity, schizophrenia, post - stroke rehabilitation, etc.," said Yuan Quan. In addition to medical - grade products and services, NuraNavX's AI brain connectomics software also supports scientific researchers in brain science research and has developed consumer - grade brain health assessment reports to reveal potential abnormalities and risks in users in advance and help patients prevent diseases.
According to data from the World Health Organization, more than 1 billion people worldwide are affected by neurological diseases. With the intensification of population aging and changes in lifestyle, the prevalence of neurological diseases is still rising. With the integrated development of cutting - edge technologies such as brain science and artificial intelligence, a number of innovative enterprises are trying to break through the bottlenecks and bring safer and more effective treatment plans to patients.
(Text | Hai Ruojing)