ZhiKe | Das Billionenmarkt der humanoiden Roboter. Welche Unternehmen an der A-Liste teilen sich den Kuchen?
Author | Fan Liang
Editor | Ding Mao
Since July, there have been frequent positive developments in the humanoid robot track.
First, on July 8, Zhiyuan Robotics and related parties planned to acquire at least 63.62% of the shares of listed company Shangwei New Materials, which was interpreted by the market as Zhiyuan's potential to backdoor list and enter the capital market. Then, on July 18, Unitree officially started the listing guidance process and released a new robot, Unitree R1, with a starting price of 39,900 yuan on July 25. Subsequently, on July 24, Elon Musk officially announced at the earnings conference that mass production of Optimus is expected to start in 2026, with a target of producing 1 million units annually within five years.
After entering August, the 2025 World Robot Conference and the first humanoid robot sports meet were held successively. According to data from the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Economy and Information Technology, the number of on - site participants at the 2025 World Robot Conference reached 271,000, and the number of people watching the live broadcast of the exhibition, competition reached as high as 52 million, a 62% increase compared to the previous session.
Although there were many voices in the market before, pointing out that there might be a bubble in humanoid robots in the short term, a series of recent intensive events indicate that the commercialization process of humanoid robots may already be underway.
Different from the primary market, in the secondary market, the "players" in the humanoid robot industry chain, except for a few complete - machine players represented by Ubtech, most participants are concentrated in the upstream and downstream of the industry chain, and they are already relatively mature listed companies with years of operation in their original business fields.
So, in other words, the purpose of these mature supply - chain companies entering the humanoid robot track is actually closer to creating a second growth curve and driving the company's industrial upgrading, and this is exactly where the expected difference of the company lies in the market.
How large is the market space for humanoid robots?
In the track investment that has emerged in recent years, the core idea is to first predict the long - term market space, then "divide the cake" according to the long - term market space, and work backward to estimate the market value space of relevant enterprises. Subsequently, operations such as increasing or reducing positions are carried out according to changes in industrial penetration rate and prosperity. Therefore, understanding the long - term space of a track is not only the starting point of track investment but also the imaginable ceiling for relevant participating companies.
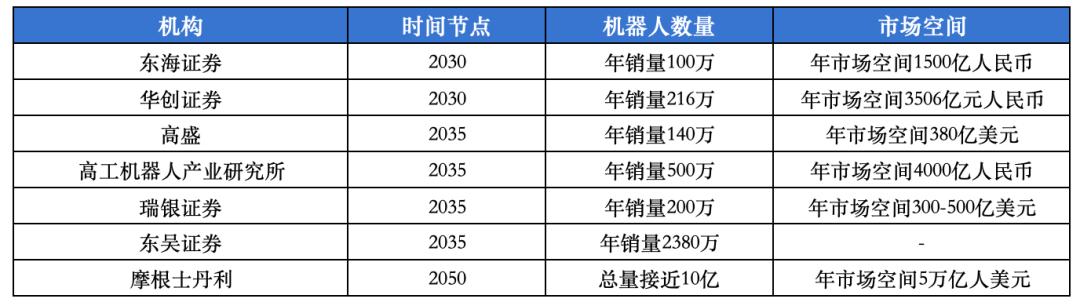
Currently, many institutions in the market have released forecasts for the industry space of humanoid robots, and there are significant variances in their long - term market forecasts for humanoid robots.
By 2030, Donghai Securities predicts that the global sales volume of humanoid robots will reach 1 million units, corresponding to a market space of 150 billion yuan, while Huachuang Securities' forecast data is nearly twice that of Donghai Securities.
By 2035, Goldman Sachs believes that the global sales volume of humanoid robots will be about 1.4 million units, corresponding to a market space of 38 billion US dollars. UBS Securities believes that the global sales volume of humanoid robots will be about 2 million units, corresponding to a market space of 30 - 50 billion US dollars, which is close to Goldman Sachs' prediction. However, Soochow Securities gives a prediction of an annual sales volume of 23.8 million units.
By 2050, Morgan Stanley believes that the global robot market space will reach 5 trillion US dollars. The well - known investment institution ARK Invest gives a more aggressive "end - game" prediction, that is, the space for humanoid robots is expected to reach 24 trillion US dollars. According to data from Zion Market Research, the global automobile sales scale in 2024 was about 23.52 trillion US dollars, which means that the long - term imagination of humanoid robots can recreate the automobile industry.
If we don't focus on the details of each institution's forecasts and only make a general trend judgment on humanoid robots in terms of total volume, then the current humanoid robot industry is in the 0 - 1 stage. In 5 - 10 years, the humanoid robot market can reach a scale of hundreds of billions, and in the more distant future, it can exceed one trillion, even surpassing the entire automobile industry.
Chart: Institutional forecasts for humanoid robot sales volume and market space. Source: Public information, compiled by 36Kr
Supported by huge imagination, in the capital market, the humanoid robot sector shows obvious event - driven characteristics. If we compare the Guojin Humanoid Robot 30 Index with the ChiNext Index, we will find that before November 2024, the trend of the humanoid robot index was basically consistent with that of the ChiNext Index, only with a relatively higher amplitude. However, after November 2024, the humanoid robot index began to show an independent trend, significantly outperforming the ChiNext Index.
There are presumably three reasons for this. First, after the "924" policy, the market's risk appetite increased significantly, and the tolerance for the valuation of the humanoid robot sector improved. Second, Tesla showed the latest video of Optimus in October 2024, and the effect exceeded market expectations. Third, the cost - reduction and efficiency - improvement of the large model brought by Deepseek led to a breakthrough in the "brain" ability of humanoid robots. Coupled with the catalysis of Unitree robots during the Spring Festival, the market showed obvious event - driven characteristics.
As a large - scale track with a long - term scale exceeding one trillion, the companies related to the humanoid robot industry chain will undoubtedly be the focus of market attention in the next few years. Behind this, there is both the support of long - term growth logic and the boost of short - term event - driven factors. In view of this, this article will sort out the A - share companies related to the humanoid robot industry, in order to provide some investment thinking for investors.
Chart: Comparison between the Guojin Humanoid Robot 30 Index and the ChiNext Index. Source: Wind, compiled by 36Kr
What are the components of a humanoid robot?
Divided by the functional modules of humanoid robots, they can be divided into three modules: the perception layer, the decision - making layer, and the execution layer.
The perception layer is equivalent to the "five senses" of the robot and is mainly composed of various sensors. It is responsible for collecting information from the external environment and the robot's own state and is the entrance for the robot to interact with the world. Specifically, it includes a vision system (cameras, lidars), a positioning and navigation system (inertial sensors, GPS, radars), a force - sensing system (six - axis force/torque sensors, joint torque sensors), and an auditory system (microphones).
The decision - making layer is equivalent to the "brain" of the robot and is mainly composed of various chips, basic models, and algorithm software. It is responsible for processing the information from the perception layer, understanding, reasoning, planning, and issuing instructions to the execution layer. Specifically, it includes processors (CPU, GPU), a cognitive system (large models and various algorithms), and motion planning and control algorithms.
The execution layer is equivalent to the "bones and muscles" of the robot and is mainly composed of various mechanical components. It is responsible for receiving and executing the instructions from the decision - making layer to complete specific physical actions, such as walking, grasping, and operating. Specifically, it includes four categories: joints, dexterous hands (coreless motors, reducers, drivers, worms, tactile sensors), skeletons (lightweight alloys, PEEK materials, carbon fiber composites), and energy systems (batteries). Among them, joints include linear joints (frameless torque motors, lead screws, drivers) and rotary joints (frameless torque motors, reducers, drivers).
From the perspective of secondary - market investment, currently, the capital market mainly trades around the hardware of humanoid robots, and the distribution of the value of humanoid robots also revolves around hardware. The reason is that it is difficult to estimate the specific cost proportion of basic models related to the decision - making layer of humanoid robots in humanoid robots, and the relevant technologies are mainly mastered by humanoid robot integrators. However, hardware supply - chain targets have clearer valuation anchors and can dynamically track the production and R & D trends in the industry.
Currently, there are mainly two ways to split the value. One is to split according to the aforementioned functional modules of humanoid robots, and the other is to split according to core components.
When splitting the value according to functional modules, according to Everbright Securities' statistics, based on a long - term unit price of 200,000 yuan, the BOM of the execution system (excluding batteries and skeletons) accounts for 53.2%, the perception system accounts for 7.3%, and other components such as chips and batteries account for a total of 39.5%. Further splitting the value of the execution system, linear joints, rotary joints, and dexterous hands account for 31.0%, 17.9%, and 4.3% respectively.
Chart: Value split of humanoid robots by functional modules. Source: Zhongtai Securities, compiled by 36Kr
When splitting the value according to core components, according to Donghai Securities, by 2030, the value proportions of the core components of humanoid robots are expected to be planetary roller screws (19%), frameless torque motors (16%), reducers (13%), torque sensors (11%), coreless motors (8%), and inertial measurement units (2%). In addition, components such as batteries, chips, radars, drivers, and encoders are grouped together as others, with a total value proportion of 31%.
Chart: Value split of humanoid robots by core components. Source: Donghai Securities, compiled by 36Kr
Which listed companies will truly benefit?
From the perspective of the industry chain, the industry chain of humanoid robots presents three major links: basic components - core modules - complete machine manufacturing. In the complete machine manufacturing link, a previous report by Morgan Stanley pointed out that it mainly includes five types of enterprises: automobile manufacturers (such as XPeng, Tesla), consumer electronics companies (such as Xiaomi), e - commerce and Internet companies, traditional robot manufacturers (such as Kuka under Midea, Estun), and emerging humanoid robot manufacturers (such as Unitree, Ubtech). Among the above - mentioned enterprises, either the original business volume is large, resulting in low investment elasticity, or they have not yet been listed on the IPO. Therefore, the market has focused its attention on the listed component manufacturers with rich targets and high elasticity.
By counting the announcements of A - share listed companies since 2023, more than 80 listed companies have stated in their announcements that they produce/plan to produce components upstream of humanoid robots.
Divided by the Wind three - level industry classification, companies in the automotive parts and machinery industries account for more than half, and the rest are scattered in fields such as electronic equipment, electrical equipment, home appliances, semiconductors, and chemicals. Divided by region, more than half of these companies are located in the Yangtze River Delta region, followed by the Pearl River Delta region, and the rest are scattered in Shandong, Sichuan, Hunan and other places.
Divided by the final components, the situation of relevant companies is as follows:
1. Planetary roller screws (value proportion is about 19%)
A screw is a transmission element that converts rotational motion into linear motion. Its technical principle is similar to "screwing a screw" in daily life. It mainly includes three categories: sliding screws, rolling screws, and hydrostatic screws. Planetary roller screws are a sub - category of rolling screws and have the advantages of high precision, high load - bearing capacity, and miniaturization.
Previously, planetary roller screws were mainly used in many industries such as automobile braking, medical devices, and construction machinery, but the market scale was relatively small. According to data from Zhiyan Consulting, in 2024, the market scale of planetary roller screws in China was 1.313 billion yuan, a year - on - year increase of 19.26%. After Tesla first used planetary ball screws in humanoid robots, the imagination space of planetary roller screws has been greatly expanded .
In terms of the market structure, according to statistics from Zhongyou Securities, in 2022, the market share of foreign leading planetary roller screw manufacturers Rollvis, GSA, and Ewellix in the Chinese market was 26%, 26%, and 14% respectively, and the total market share of Chinese domestic planetary roller screw manufacturers was 19%.
Currently, at least 17 listed companies in China have announced their layout in planetary roller screws and are mainly in the stage of R & D/raising funds for planned production.
Specifically, companies such as Inovance Technology, Changhua Group, and Hengli Hydraulics have made substantial R & D progress. Companies such as Xiaxia Precision, Wuzhou Spring, and Beit Special Technology have entered the stage of raising funds for planned production capacity. For example, Wuzhou Spring pointed out that the company plans to raise funds for projects such as an annual production of 980,000 sets of planetary roller screws, 2.1 million sets of micro - ball screws, and 70,000 sets of special bearings for general robots.
Chart: Listed companies related to planetary roller screws. Source: Company announcements, compiled by 36Kr
2. Frameless torque motors (value proportion is about 17%)
Frameless torque motors retain the parts of traditional motors used to generate torque and speed but do not have shafts, bearings, casings, or end covers. Compared with framed motors, frameless torque motors have the characteristics of small size, light weight, and high performance.
The torque motor industry, including frameless torque motors, is also a "small market". According to data from Proficient Market Insights, the global market scale of frameless brushless DC motors (including frameless torque motors) in 20